GRE Quantitative Reasoning
| Select Exercise Lists |
By Question Type
Quantitative comparison
Numeric Entry
Word Problem
Data Interpretation
By Content
Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Data Analysis
| Overview and Practice of GRE Quantitative Reasoning |
The questions are in two sorts:
- Pure mathematical problems: answer by math knowledge only
- Word problems: answer by modeling problems mathematically
- All numbers used are real numbers.
- All figures are in a plane unless otherwise indicated.
- Geometric figures are not necessarily drawn to scale.
- Coordinate systems are drawn to scale
Arithmetic Topics include properties and types of integers, arithmetic operations, exponents and roots, and concepts of estimation, percent, absolute value, the number line, and decimal representation.
| 1/5 | |
| 6/5 | |
| 63 | |
| 64/5 | |
| 64 |
Algebra Topics include operations with exponents; algebraic expressions; equations and inequalities; linear and quadratic equations and inequalities; and coordinate geometry, including graphs of functions, intercepts and slopes of lines.
| 5 - 2√ 6 | |
| 5 - √ 6 | |
| 1 - 2√ 6 | |
| 1 - √ 2 | |
| 1 |
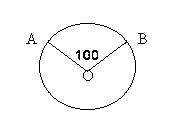
Geometry Topics include parallel and perpendicular lines, circles, triangles, quadrilaterals, other polygons, three-dimensional figures, area, perimeter, volume, and angle measurement in degrees. (Not need to construct proofs of geometry.)
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 |
Data Analysis Topics include basic descriptive statistics; interpretation of data in tables and graphs; elementary probability; conditional probability; random variables and probability distributions, including normal distributions; and counting methods, such as combinations and permutations.
| 6 | |
| 15 | |
| 24 | |
| 33 | |
| 54 |
Quantitative Comparison is the primary type in GRE quantitative reasoning and usually ask you select one answer choice from multiple options.
Exercises of quantitative comparisonQuantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
A symbol that appears more than once in a question has the same meaning throughout the question.
| For any positive integer n, π(n) represents the number of factors of n, inclusive of 1 and itself. a and b are prime numbers | |
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
| πA + πB | π(a × b) |
| Quantity A is greater. | |
| Quantity B is greater. | |
| The two quantities are equal. | |
| The relationship cannot be determined without further information. |
Numeric Entry needs you calculate the answer; some Words Problem question also needs you give the numeric answer after modeling.
Exercises of numeric entryWord Problem emphasizes to translate the problem to the mathematical model, you need to calculate the answer, select one or more choices from multiple options.
Exercises of word problem| 1/2 | |
| 2/10 | |
| 1/50 | |
| 1/500 | |
| 2/500 |
Data Interpretation usually has a set of questions based on the same data source; the problems are diversity, like calculating the answer, selecting one or more choices from multiple options.
Exercises of data interpretation
| 34 | |
| 38 | |
| 40 | |
| 45 | |
| 68 |
| 1 | |
| 3/2 | |
| 2/3 | |
| 1/5 | |
| 5/4 |
| Sponsored Links |